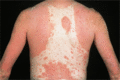
Figure 35.1
Although sunlight is generally beneficial, psoriasis may be provoked by sunlight in a minority. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, Lond...
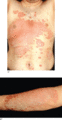
Figure 35.5
(a,b) Psoriasis is characterized by well‐demarcated red scaly plaques.
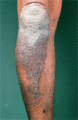
Figure 35.9
In dark‐skinned races, the quality of the colour is lost. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)

Figure 35.13
(a) The disease often first appears in the scalp, where it may present as pityriasis amiantacea. (b) Pityriasis amiantacea in psoriasis. (Courtesy of...
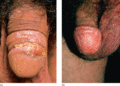
Figure 35.17
(a) Penile psoriasis in a circumcised man. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Penile psoriasis in a circumcised man re...
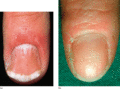
Figure 35.21
(a) Fingernail pitting in psoriasis. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Psoriatic nail pitting.
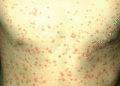
Figure 35.25
Extensive lesions of guttate psoriasis in a young man.
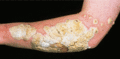
Figure 35.29
Elephantine psoriasis: large plaques with gross hyperkeratosis. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
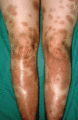
Figure 35.33
Staining produced by dithranol.
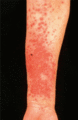
Figure 35.37
Acute generalized pustular psoriasis: pre‐existing psoriasis plaques become fiery and develop pinpoint pustules. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of ...
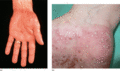
Figure 35.41
(a) Acute palmoplantar pustulosis. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Acute palmoplantar pustulosis.
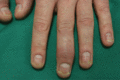
Figure 35.45
Distal interphalangeal involvement.
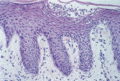
Figure 35.2
Psoriasis: intraepidermal spongiform pustule (of Kogoj). H&E, ×100. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
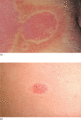
Figure 35.6
(a,b) Plaques may be encircled by a clear peripheral zone, the halo or ring of Woronoff.
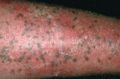
Figure 35.10
Lentigines in a plaque of psoriasis.
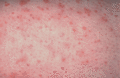
Figure 35.14
Psoriasis around hair follicle openings (follicular psoriasis).
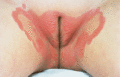
Figure 35.18
Well‐demarcated thin plaques of psoriasis affecting the labia majora. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
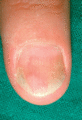
Figure 35.22
Salmon patches (‘oil drops’), with distal onycholysis.
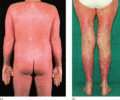
Figure 35.26
(a) Acute unstable erythrodermic psoriasis. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Extensive tender fiery red plaques of u...
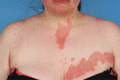
Figure 35.30
Segmental psoriasis.
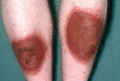
Figure 35.34
Irritation produced by dithranol.
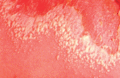
Figure 35.38
Acute generalized pustular psoriasis of von Zumbusch.
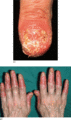
Figure 35.42
(a) Acrodermatitis continua with destruction of the nail plate. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Acrodermatitis cont...
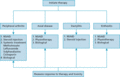
Figure 35.46
The Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) management guidelines for psoriatic arthritis. NSAID, non‐steroida...

Figure 35.3
Psoriasis: Munro microabscess formation in lesional stratum corneum. H&E, ×200. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
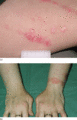
Figure 35.7
(a) Koebner phenomenon. Psoriasis appearing in the line of a scratch. (b) Psoriasis provoked by the friction of wearing a watch.
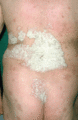
Figure 35.11
Most plaques of psoriasis are surmounted by silvery white scaling, which varies considerably in thickness.
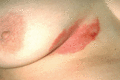
Figure 35.15
Submammary flexural psoriasis.
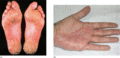
Figure 35.19
(a) On the palms and soles, psoriasis may present as typical scaly plaques. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b) Typical...
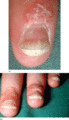
Figure 35.23
(a) Psoriatic subungual hyperkeratosis with distal onycholysis. (b) Marked psoriatic subungual hyperkeratosis.
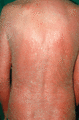
Figure 35.27
Erythrodermic psoriasis in an older man.
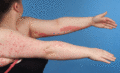
Figure 35.31
Linear psoriasis on the left upper limb associated with guttate psoriasis on the right upper limb.

Figure 35.35
Pustulation in unstable psoriasis – ‘psoriasis with pustules’ – rather than pustular psoriasis.
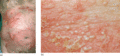
Figure 35.39
(a) Subacute annular generalized pustular psoriasis. (b) Monomorphic non‐follicular pustules of generalized pustular psoriasis (von Zumbusch).
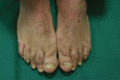
Figure 35.43
Dactylitis.
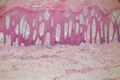
Figure 35.4
Psoriasis irregular epidermal hyperplasia with suprapapillary thinning. H&E, ×50. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
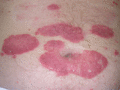
Figure 35.8
The colour of the plaques, a full rich red. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.)
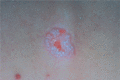
Figure 35.12
Auspitz sign: removal of the thinned suprapapillary epidermis by gentle scraping reveals vascular bleeding points. (Courtesy of St John's Institute o...
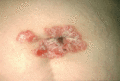
Figure 35.16
Flexural psoriasis affecting the umbilicus.
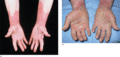
Figure 35.20
(a) A sharply defined edge at the wrist or forearm and absence of vesiculation are helpful diagnostic features. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of D...
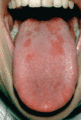
Figure 35.24
Geographic tongue in a patient with psoriasis.
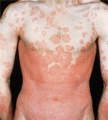
Figure 35.28
Erythroderma in psoriasis may be chronic, due to the gradual progression of extensive plaque psoriasis. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatolo...
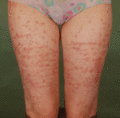
Figure 35.32
Striae induced by potent topical corticosteroids in psoriasis.
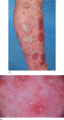
Figure 35.36
(a) Inflammatory unstable psoriasis; (b) close‐up of pustules on dermoscopy.
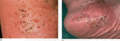
Figure 35.40
(a) Palmoplantar pustulosis. Normally, pustules in all stages of evolution are seen. (Courtesy of St John's Institute of Dermatology, London, UK.) (b...
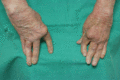
Figure 35.44
Arthritis mutilans.

