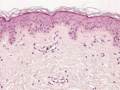
Figure 53.1
Skin histopathology (medium power). There is a mild lichenoid tissue reaction with subtle vacuolar change in the basal layer and occasional Civatte bo...
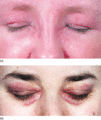
Figure 53.5
Eyelid involvement in DM. (a) There is lilac erythema of the upper eyelids, which are also oedematous. In this patient with DM the facial skin is gene...
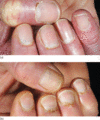
Figure 53.9
The nail folds and cuticles are usually affected in dermatomyositis. (a) Dilated nail fold capillary loops are visible. (b) The cuticles are hypertrop...
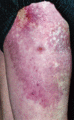
Figure 53.13
The dermatosis of dermatomyositis can affect the gluteal skin and proximal thighs. Involvement of the skin overlying the hips is known as the holster ...
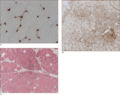
Figure 53.2
Muscle biopsy. (a) Capillary staining for C5b‐9, the membrane attack complex, is an early pathological finding in dermatomyositis. (b) Diffuse up‐regu...
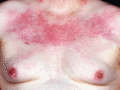
Figure 53.6
The upper chest is a common site of skin involvement in dermatomyositis.
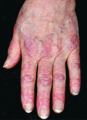
Figure 53.10
Gottren's papules: violaceous, flat‐topped, shiny papules on the skin overlying the interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints.
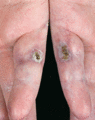
Figure 53.14
Vasculopathic ulcers, which have dusky margins and are ‘punched‐out’, may occur in DM patients, particularly those who are positive for anti‐MDA5 anti...
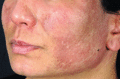
Figure 53.3
Facial erythema in dermatomyositis is often widespread and can mimic many dermatoses, including lupus erythematosus.
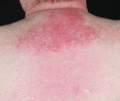
Figure 53.7
Erythema of the upper central back is known as the shawl sign.
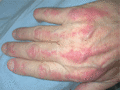
Figure 53.11
There are streaks of erythema on the dorsal aspects of the fingers, extending onto the backs of the hands.
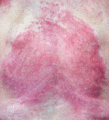
Figure 53.15
In severe dermatomyositis, skin involvement on the torso can become extensive and fixed.

Figure 53.4
A diffuse, non‐scarring alopecia is common in dermatomyositis. The scalp is inflamed with violaceous erythema and mild scaling.
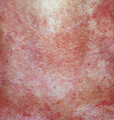
Figure 53.8
Poikiloderma occurs in dermatomyositis; it is composed of telangiectatic erythema, epidermal atrophy and dyspigmentation.
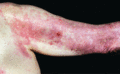
Figure 53.12
Involvement of the extensor surfaces of the arms is typical in dermatomyositis.
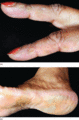
Figure 53.16
Non‐inflammatory hyperkeratosis occurring on (a) the fingers and (b) the feet may be seen in Jo‐1‐positive DM. Involvement of the radial surfaces of t...

