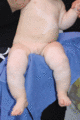
Figure 70.1
Typical body and limb pattern of hypopigmentation in piebaldism.

Figure 70.5
(a,b) Oculocutaneous albinism type 1B (OCA1B) and siblings/family. (a) The children in the centre and on the right are affected; the child on the left...
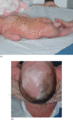
Figure 70.9
(a,b) Albinism–deafness syndrome. (Courtesy Dr Odile Enjolras.)
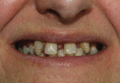
Figure 70.13
Dystrophic teeth in the carrier mother of a child with incontinentia pigmenti.
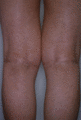
Figure 70.17
Dowling–Degos disease.

Figure 70.21
(a,b) Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria (molecular diagnosis not done).
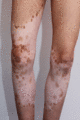
Figure 70.2
Partial repigmentation pattern on the legs in piebaldism.

Figure 70.6
(a) Oculocutaneous albinism type 1A (OCA1A) at birth and (b) later in the same child.
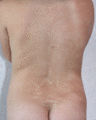
Figure 70.10
Hypomelanosis of Ito.
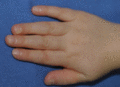
Figure 70.14
Nail dystrophy of incontinentia pigmenti.
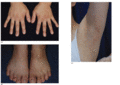
Figure 70.18
(a–c) Reticulate hyperpigmentation of Kitamura. (Courtesy of Dr H. Ujiie and Professor H. Shimizu.) Molecular diagnosis was confirmatory.

Figure 70.3
(a) Note the mosaic pattern on the trunk in piebaldism; (b) detail of repigmentation pattern (leg).

Figure 70.7
Oculocutaneous albinism type 2 (OCA2) in infant (shown with mother).

Figure 70.11
Linear and whorled naevoid hypermelanosis.

Figure 70.15
Cicatricial alopecia of incontinentia pigmenti.
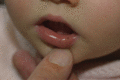
Figure 70.19
Peutz–Jeghers–Touraine syndrome. Lentigines on the lower lip of a 2‐year‐old girl.
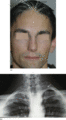
Figure 70.4
Typical facial dysmorphic features (a) and supernumerary ribs (b) in Waardenburg syndrome.

Figure 70.8
Chédiak–Higashi syndrome after successful bone marrow transplantation: mild mental retardation and hair pigment dilution.
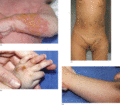
Figure 70.12
(a) Incontinentia pigmenti, vesiculobullous stage, frequently wrongly diagnosed as bullous impetigo. (b) Verrucous stage. (c) Pigmentary stage, with a...
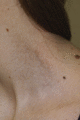
Figure 70.16
Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome: case of the original family. (Courtesy of P. Itin.)
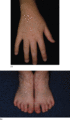
Figure 70.20
(a,b) Dyschromatosis symmetrica hereditaria. (Courtesy of Dr H. Ujiie and Professor H. Shimizu.) Molecular diagnosis was confirmatory.

